UC Davis School of Medicine tests potential COVID-19 treatments and vaccines
by Nadine Yehya
With more than 41.5 million cases and a year and a half after the first confirmed COVID-19 case in the U.S, the search for a safe and effective cure to coronavirus continues.
As the pandemic spread around the globe, researchers at the School of Medicine partnered with drug developers and funding agencies to find and test potential therapies and vaccines to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
“UC Davis School of Medicine, renowned for its research expertise, is a trusted partner on many COVID-19 clinical trials and research studies. We are immensely grateful to all our researchers who continue to be at the forefront of efforts to cure this terrible disease,” said Allison Brashear, the dean of the UC Davis School of Medicine.
UC Davis received about $42 million in COVID-19 research funds in 2020-21. The School of Medicine’s share was more than two-thirds of that, nearly $28.5 million.
With more than 75 COVID-19 research grants, the School Medicine conducted at least 28 studies to find potent treatments and vaccines.
COVID-19 vaccine testing
The UC Davis School of Medicine has played in instrumental role in testing potential COVID-19 vaccines, including the now FDA-approved Pfizer vaccine for adults and the under-review Novavax vaccine for adults and children (12-17 years old).
Currently, researchers are testing a booster COVID-19 Pfizer shot to adults. They are also assessing SARS CoV-2 infection, viral shedding and potential transmission in young adults immunized with the Moderna’s vaccine.
Ongoing clinical trials for potential COVID-19 treatments
UC Davis School of Medicine researchers are currently recruiting for multiple clinical trials, including those using stem-cell-based therapies, monoclonal antibodies, and other experimental drugs. These include:
- Capricor’s IV drug: This study tests how well intravenous infusions of CAP-1002 work in hospitalized patients with coronavirus. CAP-1002, based on cardiac stem cell tissues, could decrease inflammation, block or prevent tissue scarring, and stimulate new tissue growth.
- AT-527: This study tests the efficacy and side effects of AT-527 drug, an oral antiviral experimental drug, in hospitalized people with COVID-19.
- Remdesivir and other medications (I-SPY COVID): This study seeks to determine if the antiviral drug remdesivir used alone or in combination with other drugs can treat COVID-19 and reduce the recovery time for those with severe symptoms.
- ACTIV-3: This publicly funded study tests several agents against COVID, among them, AstraZeneca’s experimental antibody (AZD7442) and Pfizer’s antiviral drug (PF-07304814) to see if these can reduce the severity of the disease and shorten hospital stays for people with COVID-19.
- Selinexor (KPT-330): This study is investigating whether Selinexor, an FDA-approved drug for treating multiple myeloma, speeds up the recovery of COVID-19 patients and reduces their viral load, hospital stay, and complications or chance of dying, compared to standard of care treatment.
- Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody cocktail: This study is looking at Regeneron’s combined monoclonal antibodies (REGN10933 + REGN10987) as a treatment for non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Monoclonal antibodies are a special kind of manufactured antibodies that restore, enhance, or mimic the natural immune system. These antibodies are also being tested for household members of patients with COVID-19.
- Isavuconazole to prevent COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: This study is to find out more about the prevention of fungal infections, specifically aspergillosis, in people with COVID-19 infection. Researchers are testing whether the drug isavuconazole can decrease the time COVID patients stay in the ICU and the hospital.
- Experimental stem cells for the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): This publicly-funded trial aims to see how effective mesenchymal stromal cells – a type of stem cells – are in reducing inflammation associated with ARDS and in helping damaged lungs repair themselves. ARDS is one of the severe complications of COVID-19 infection.
The researchers also concluded recruitment for multiple clinical trials, including:
- Molnupiravir (MK-4482): The study tests an experimental antiviral drug called molnupiravir (MK-4482) in patients with COVID-19. Molnupiravir, by Ridgeback Biotherapeutics and Merck & Co, is taken orally, making it easier to use and distribute.
- Otilimab in severe COVID-19 related disease (OSCAR): This trial assesses the efficacy and safety of GSK’s otilimab drug for the treatment of severe pulmonary COVID-19 related disease.
- Cell therapy to treat patients with COVID-19: This study tests how well a treatment with natural killer cells (CYNK-001) works in people with COVID-19. Natural killer cells from the human placenta are immune cells known to kill some types of cancers without hurting normal healthy tissues.
- Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody cocktail: This study tested Regeneron’s combined monoclonal antibodies as a treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
- Pfizer IV drug in hospitalized patients: The study tests the safety and efficacy of the PF-07304814 drug in hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
- Intramuscular injections of PLX-PAD: The study evaluates injections of stromal cells (called PLX-PAD) in the muscle for the treatment of severe COVID-19 patients. It tests if PLX-PAD can help patients intubated and on ventilators due to COVID-19 recover faster with fewer complications. PLX-PAD cells, extracted from the human placenta, have regenerative potential that might help reduce tissue damage caused by hyperimmune reaction to coronavirus.
“We take this opportunity to thank all of the participants who volunteer in our clinical trials,” said Timothy Albertson, chair of internal medicine at UC Davis School of Medicine and principal investigator on multiple COVID-19 clinical trials. “Their contribution helps to save lives and push science forward.”
Learn more about how to sign up for UC Davis Health clinical trials or studies here.
COVID-19 studies at California National Primate Research Center
The California National Primate Research Center (CNPRC) is also active in COVID-19 research. Its researchers are studying the early immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and testing juvenile COVID-19 vaccine in primates. Another research study focuses on developing vaccine strategies specifically for patients with diabetes mellitus. These patients have a particularly high risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome and increased mortality.
Developing rapid COVID-19 tests
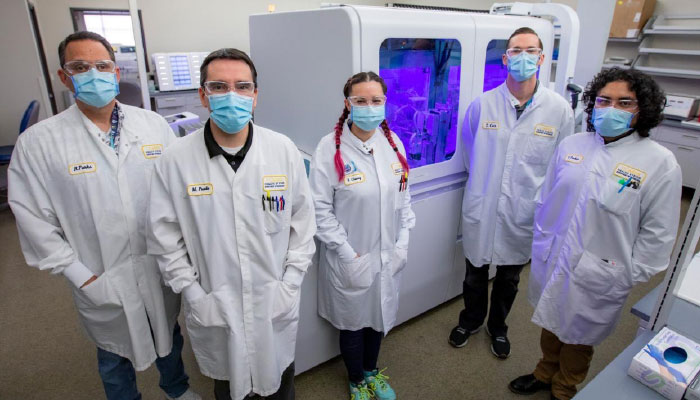
The Molecular Pathology team developed COVID-19 testing on the Roche Diagnostics cobas 6800 System in just 19 days. (Wayne Tilcock/UC Davis)
With the advent of the pandemic, clinical lab scientists at UC Davis Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine developed an in-house COVID-19 test. Their remarkable achievement was a testament to a great interdisciplinary teamwork culture spanning across many departments.
One notable collaboration between UC Davis School of Medicine and the industry is the development of a rapid COVID-19 test. The new test uses an analytical instrument known as a mass spectrometer, which is paired with a powerful machine-learning platform to detect SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swabs.
Caption: Rapid COVID-19 test uses robotics and machine learning
Latest News & Events